Aerial imagery collected in the central geodetic and cartographic resource (czgik) are images of the terrain surface obtained using specialized cameras installed on board the plane.
According to regulation of December 16, 2022 on databases for aerial and satellite imagery, orthophotomap and digital terrain models, photogrammetric aerial imagery are collected in czgik:
• vertical, constituting a registered and recorded image of the Earth’s surface, made from the ceiling of an airplane with an angle of deviation of the main axis of the camera from the vertical line of no more than 5°.
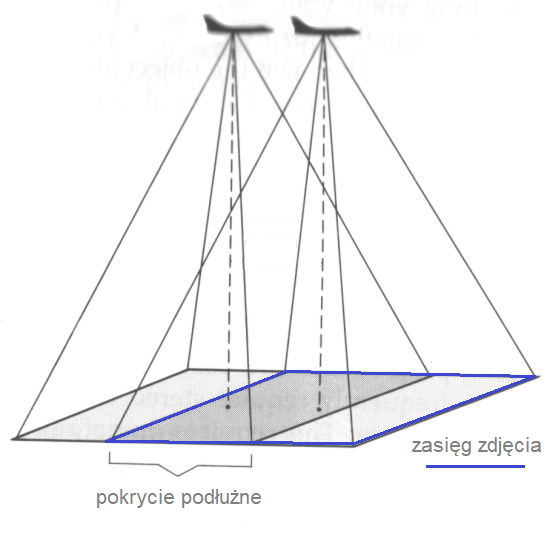
They have a longitudinal coverage of at least 60% and a transverse coverage of at least 30%, so that each part of the terrain is photographed in at least two imagery.
• oblique, which is a registered and preserved image of the Earth’s surface, made from the ceiling of an airplane with an angle of deviation of the main axis of the camera from the vertical line of not less than 35° and not more than 50°.
Oblique aerial imagery, unlike vertical aerial imagery, allow you to reproduce, for example, building facades. Oblique aerial imagery are taken with a longitudinal coverage of at least 80% and a transverse coverage of at least 60%. This coverage guarantees that the same point is photographed in more than 10 imagery.
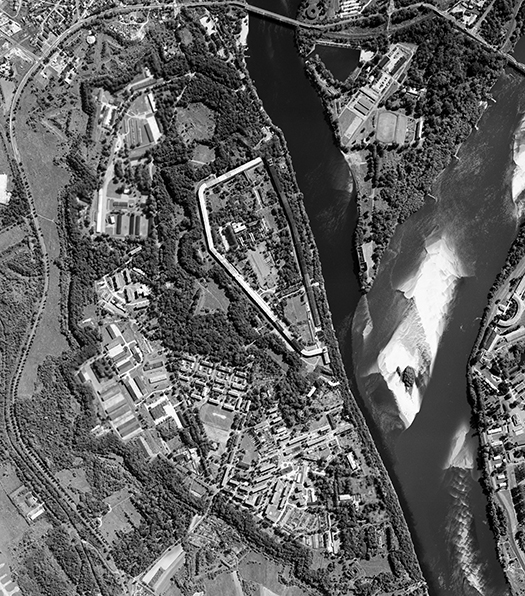
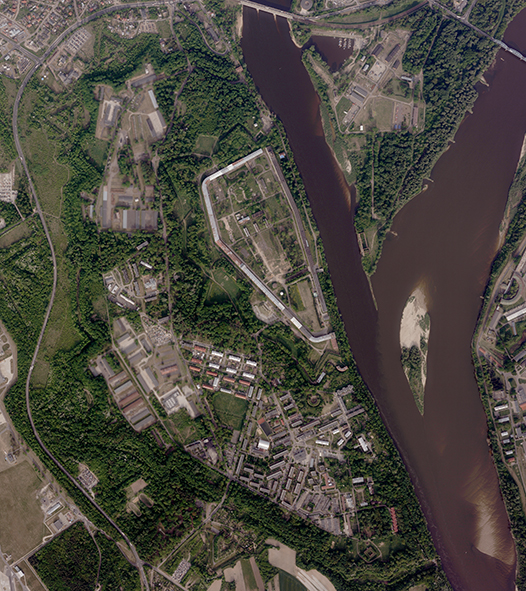
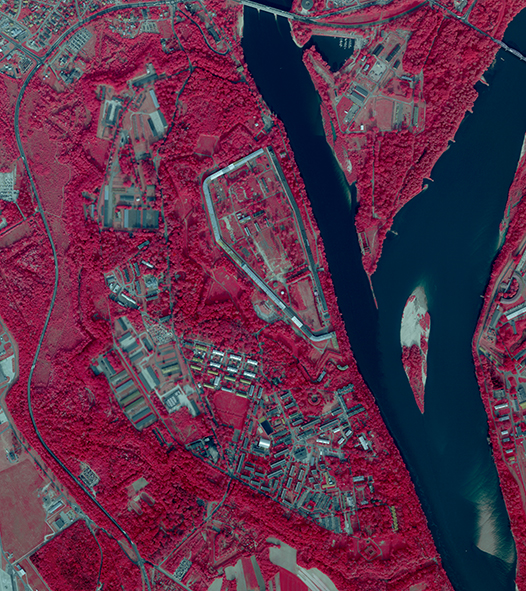
Czgik offers aerial imagery taken with digital cameras (recorded in the form of digital rasters), as well as archival aerial imagery obtained with analog cameras (recorded on photosensitive material). These imagery are characterized by a field pixel size (GSD) from 3 to 50 cm (imagery taken with a digital camera) or a scale from 1:3,000 to 1:35,000 (imagery taken with an analog camera) and various color compositions: black and white (B/W), colored (RGB), infrared (CIR).
Aerial imagery are taken to illustrate the area at a given moment and processed into intermediate products, mainly orthophotomap or other spatial data and maps. The oldest aerial imagery available from czgik date from 1951.
Aerial imagery has a wide range of applications, including:
• to create vector maps using photogrammetric measurement
• to develop an orthophotomap
• to develop numerical elevation data (DTM, NMPT) for the interpretation, identification and measurement of elements appearing in the image, including those that change over time
• as evidence in court and administrative proceedings
• as historical material presenting Poland in recent years.
Availability of aerial imagery
Information about aerial imagery available at any given time is presented on the website www.geoportal.gov.pl in the Indexes section in the Aerial Imagery layer group (Fig. 3).
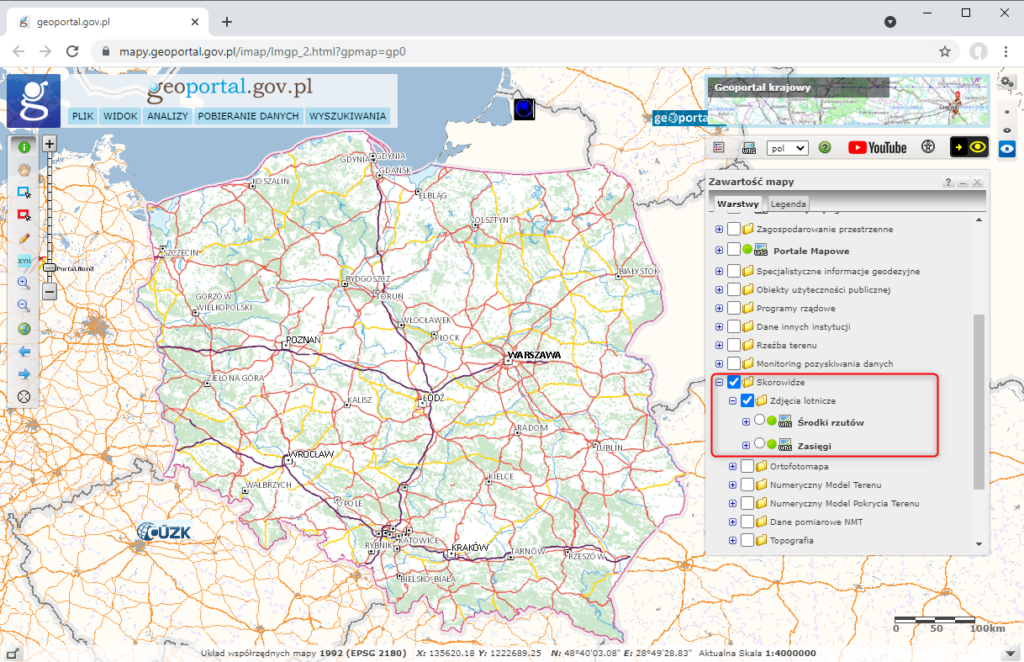
The Aerial Imagery layer group contains two layers:
- Centers of projections – individual layers of aerial imagery present the centers of projections of aerial imagery since 1951, divided into 5-year intervals (Fig. 4).
- Ranges – currently, the individual layers present the ranges of aerial imagery since 1991 in 5-year intervals. The layer will be successively fed with older aerial imagery ranges (Fig. 5).
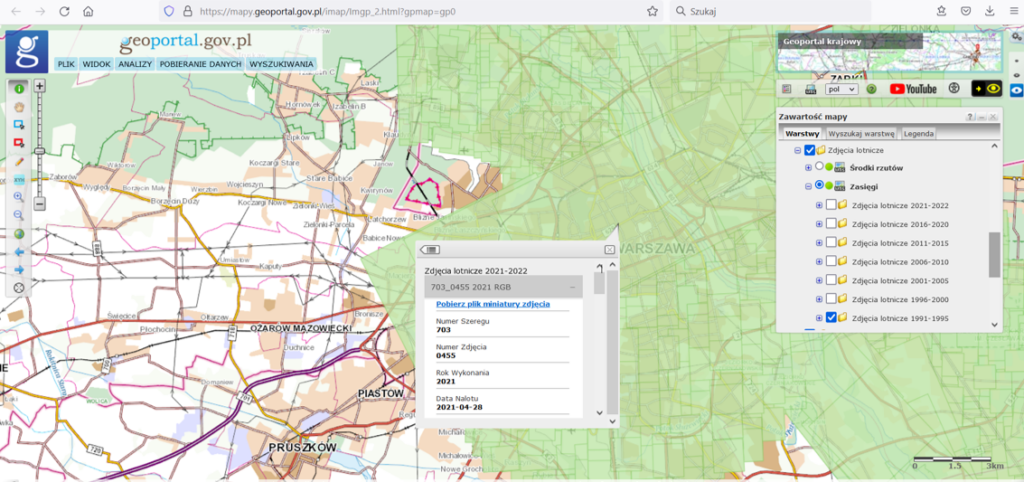
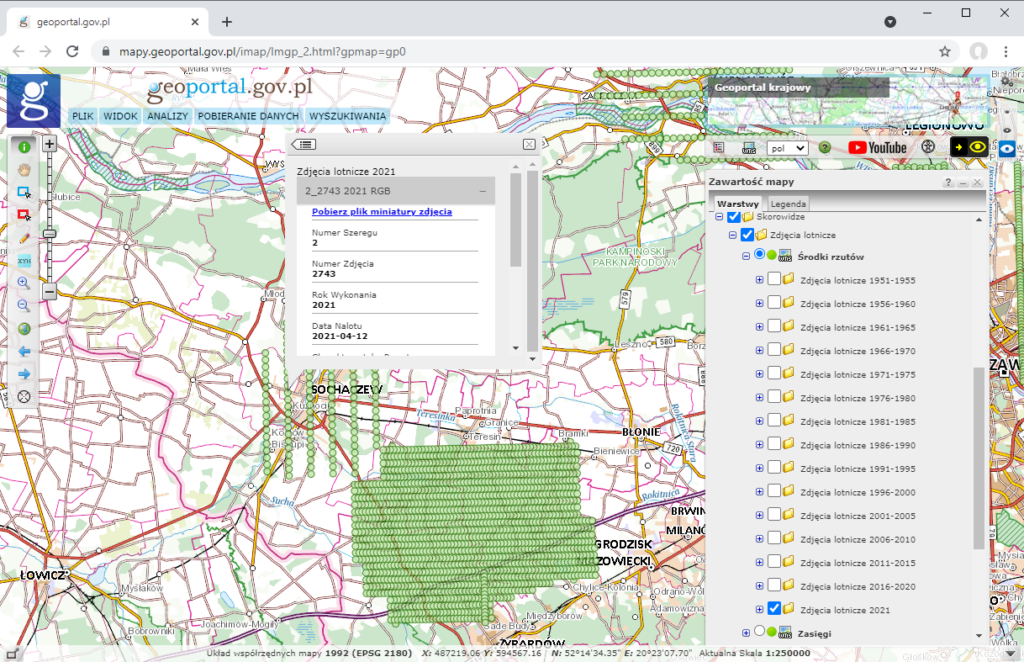
After turning on one of the above-mentioned layers and zoom in to the place of interest (at least to a scale of 1:250,000), available aerial imagery from the selected years will be visible. Then click on the selected aerial imagery and detailed information about the imagery will appear on the screen, as illustrated in the figures above.
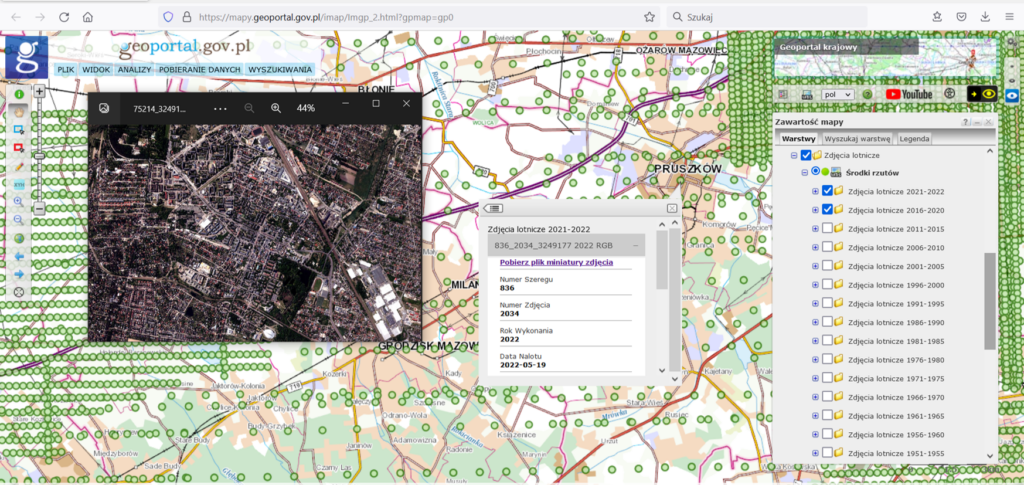
Additionally, the user can preview each aerial imagery by downloading their miniatures in jpg format, i.e. aerial imagery saved in low resolution, using the “Download imagery miniatures file” function. As a result of the described actions, a file with aerial imagery miniatures will be downloaded to the user’s computer and displayed in the default image file browser, as shown in Fig. 6.
Aerial imagery in full resolution can be obtained online for a fee via the PZGIK portal (Fig. 7) by creating a user account https://pzgik.geoportal.gov.pl/imap/ and submitting an appropriate application.